More than 11 million HTTPS websites at risk of new DROWN attack
After the deadly Heartbleed vulnerability which shook the world last year, another critical vulnerability is looking ominous to create similar fears. A recently discovered OpenSSL security hole enables an ancient, long deprecated security protocol, Secure Sockets Layer (SSLv2), to be used to attack modern web sites.
Readers should understand the seriousness of the the vulnerability as almost all of banks, financial institutions and other websites which gather personal identifiable information (PII) use HTTPS for secure communication between the user and the web server.
The attack exploiting this, dubbed DROWN(Decrypting RSA with Obsolete and Weakened eNcryption), is estimated to be able to kill off at least one-third of all HTTPS servers. The researchers who discovered the flaw stated that as many as 11.5 million websites who use the HTTPS protocol may be at risk from DROWN attack.
DROWN attack was uncovered by academic researchers from Department of Electrical Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Münster University of Applied Sciences, Horst Görtz Institute for IT security, Ruhr University Bochum, University of Pennsylvania, Hashcat Project, University of Michigan, Two Sigma/OpenSSL, Google/OpenSSL.
The researchers stated that “We’ve been able to execute the attack against OpenSSL versions that are vulnerable to CVE-2016-0703 in under a minute using a single PC. Even for servers that don’t have these particular bugs, the general variant of the attack, which works against any SSLv2 server, can be conducted in under 8 hours at a total cost of $440.”
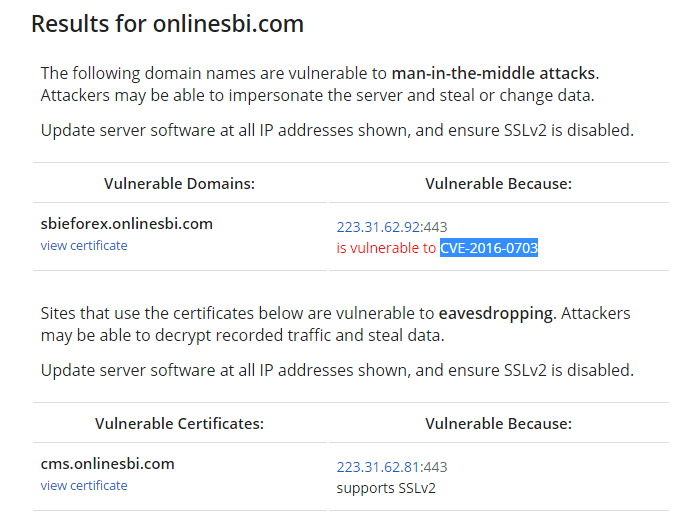
As of now, some of the top web sites listed on Alexa are vulnerable to DROWN-based man-in-the-middle attacks, including Yahoo, Sina, and Alibaba. Even India’s premier bank State Bank of India is vulnerable to CVE-2016-0703 (MitM attack) which allows potential hackers to decrypt recorded traffic and steal data.
The researchers said that obsolete Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) versions 7 and earlier are vulnerable, and editions of Network Security Services (NSS), a common cryptographic library built into many server products prior to 2012’s 3.13 version, are also open to attack.
You can find out if your site is vulnerable using the DROWN attack test site.
In any case, if you use OpenSSL for security, now is the time to upgrade to 1.0.2g. OpenSSL 1.0.1 users should also upgrade to version 1.0.1s.