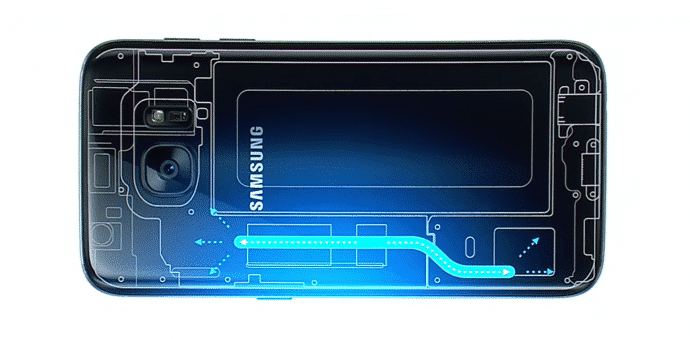
A clever liquid cooling system will keep Samsung Galaxy S7 from overheating
Overheating is a major problem that OEMs are faced with high-processing devices. The GPU (graphics processor, for gaming) and CPU (processor) are primary contributors to the increase in temperature, because with more power comes more heat.
The Galaxy S7 has some of the latest, fastest, and most powerful specs in a smartphone, which means that the entire horsepower would create more heat than usual. To prevent overheating, Samsung has deployed a liquid cooling system to the Galaxy S7.
“For the first time Samsung has established within the smartphone heat-conducting copper tube for cooling. The new chip Exynos 8890 is not only powerful, but also hot!” the blog says.
Samsung’s Senior Vice President of product strategy, Justin Denison during the S7’s announcement at MWC (Mobile World Congress) termed the liquid cooling system as “air conditioning for your phone.”
“There’s a tube containing a liquid that vaporizes at high temperatures and then condenses at low temperatures,” he explained.
So, how does the feature work? Samsung is using what is called a heat pipe, and while it does involve a tiny bit of liquid, it is of course not anything much like a full-scale desktop PC water cooling system.
The Samsung Galaxy S7 phones’ water cooling technology is reportedly based on a very thin “thermal spreader” sealed inside the phones that uses water evaporation and condensation to avoid the phones from overheating and cool them down more effectively. This allows the CPU and GPU to work more efficiently and deliver enhanced performance, thus avoiding any chance of overheating, freezes or shortened motherboard lifespan.
“Obviously the scale is miniature compared to desktop water cooling, but the sealed copper cooling system will still do its best to shift excess heat away from the S7’s processor when games push things to the phone’s thermal limits,” reports CNET.
In case of iPhone, the device automatically switches itself off, if it detects that it’s close to overheating to protect the components inside.